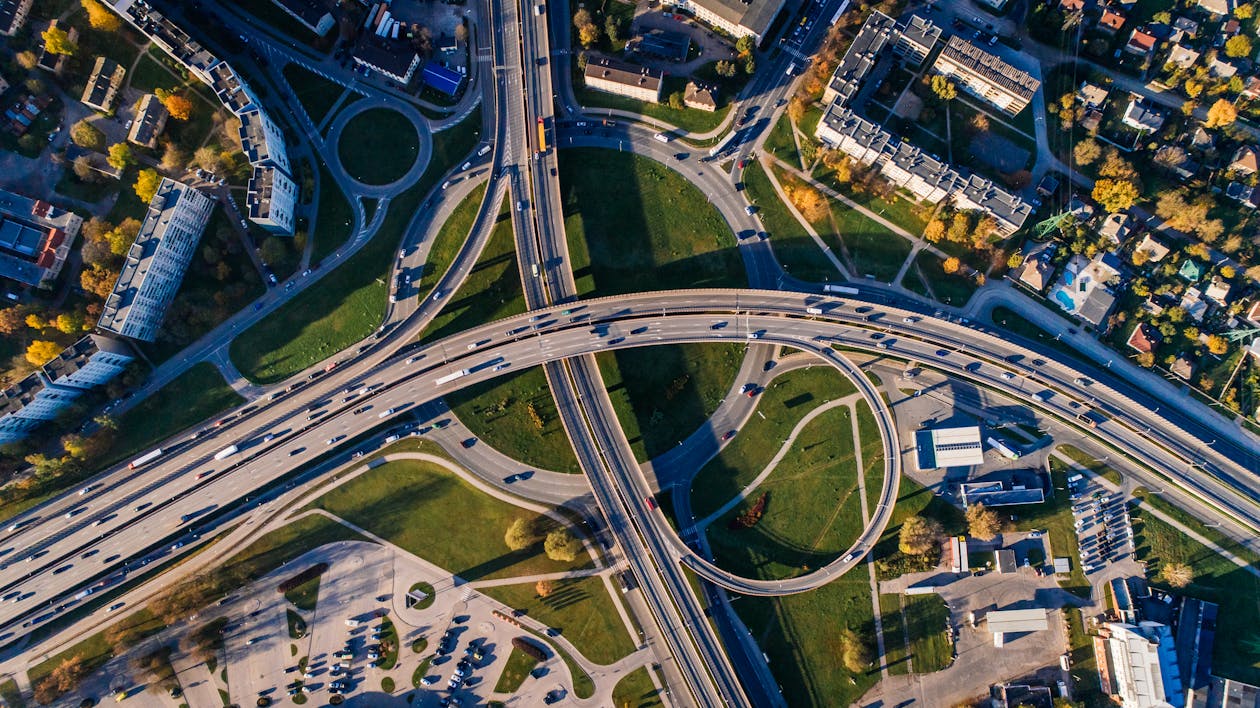

Aerial photography, at its core, captures the world from a bird’s-eye view, providing a unique and comprehensive perspective that ground-level shots cannot achieve. Over the years, this technique has proven invaluable across numerous sectors, ranging from urban planning to environmental research.
Its ability to offer a holistic overview has made both aerial photos and imagery of it a sought-after tool for professionals in diverse fields, highlighting not only the beauty of our planet but also revealing patterns, changes, and insights that might otherwise remain hidden. As technology evolves, so does the realm of aerial photography and satellite images, continuously expanding its significance and potential applications in our ever-changing world.
The Drone I Use
Mavic 3 Pro: https://amzn.to/3Bdk6mc
Methods and Tools Used in Aerial Photography

Aerial photography, as a specialized form of capturing images, requires unique tools and methods to effectively photograph landscapes, events, or structures from an elevated perspective. The methodology of aerial photographs has evolved considerably since its inception, with advances in technology presenting an array of equipment options. These platforms offer a diverse range of vantage points and functionalities, suited to various needs artistic projects and purposes. Let’s delve into some of the most widely-used methods and tools in the world of aerial photography.
Aircraft (planes and helicopters)
-
Use Cases: Ideal for covering large areas, these are often used for topographical surveys, wildlife monitoring, and high-altitude photography.
-
Advantages: They can carry heavier camera equipment, offer a stable platform, and can travel long distances.
-
Limitations: Operating costs can be high, and they may be less suitable for low-altitude or close-up shots.
Drones/UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles)
-
Use Cases: Drones are versatile and are used for real estate photography, event coverage, agriculture surveys, and more.
-
Advantages: They are cost-effective, can maneuver in tight spaces, and provide real-time feedback to operators. Moreover, drones can access hard-to-reach areas.
-
Limitations: Battery life can be limited, and there are regulatory restrictions in many regions to ensure safety and privacy.
Balloons and Blimps
-
Use Cases: Often used for promotional events, tourism, and sometimes for slow-moving aerial coverage of an area.
-
Advantages: They offer a serene and slow-moving platform, which can be great for capturing stable shots.
-
Limitations: They are dependent on wind conditions, have limited mobility, and might not be suitable for detailed, high-resolution surveys.
Satellites
-
Use Cases: Used for large-scale earth observation, weather forecasting, and mapping applications like Google Earth.
-
Advantages: Can cover vast areas, operate in a geostationary position, and can be equipped with multispectral sensors.
-
Limitations: High costs for launching and maintenance, and might not be suitable for low-altitude, detailed imagery.
Types of Aerial Photography Based on Purpose

Aerial photography is an ever-evolving field that serves a multitude of purposes. With the vantage point from above, it provides perspectives that ground-based photography simply cannot achieve. From understanding the contours of the land to capturing the grandeur of architectural marvels, aerial photography is instrumental in various domains. The specific intent or goal of the shoot often dictates the type of aerial photography deployed. Let’s dive deeper into the different types of high oblique photographs and vertical photographs, based on their primary purpose:
a. Survey and Mapping
-
Topographic Maps: Aerial images are used to illustrate the contours, elevations, and features of the terrain. These maps are critical for civil engineering projects, hiking trails, and urban planning.
-
Cadastral Maps: Focus on property boundaries and land ownership, often used by governments for land registration and taxation purposes.
-
Hydrological and Environmental Studies: Enables study of water bodies, wetlands, and watersheds, providing invaluable data for conservation and water resource management.
b. Real Estate and Architecture
-
Property Showcases: Capture properties from a bird’s-eye view, showcasing the scale, layout, and surrounding areas, enhancing real estate listings.
-
Architectural Documentation and Design Planning: Used by architects and designers to understand the landscape and plan around existing structures or natural features.
c. Agriculture
-
Crop Health Assessment: Utilizing multispectral imaging, aerial photography can detect crop health, ensuring timely interventions.
-
Irrigation Planning: Helps in designing effective irrigation systems by understanding the topography.
-
Pest and Disease Detection: Early detection of infestations or disease can save vast portions of crops, preserving yield and profit.
d. Environmental and Conservation
-
Wildlife Tracking: Monitor and study wildlife in their natural habitat, aiding conservation efforts.
-
Habitat Assessment: Understand and assess the quality of habitats, crucial for preservation and restoration projects.
-
Deforestation and Land Degradation Monitoring: A critical tool for monitoring environmental health and ensuring sustainable practices.
e. Commercial and Advertising
-
Brand Commercials: Brands utilize aerial shots for their grandeur and scale, making advertisements more compelling.
-
Event Coverage: Capture the magnitude of events, festivals, or concerts, offering viewers a holistic perspective.
-
Film and Entertainment: Aerial shots have become a staple in films for chase scenes, landscape shots, and more, adding dramatic effect.
f. Journalism and News
-
Disaster Assessment: In the aftermath of natural calamities like floods, fires, or earthquakes, aerial photography provides a quick assessment of the damage, aiding rescue and relief operations.
-
Event Coverage: Be it parades, protests, or large public gatherings, aerial views provide a comprehensive understanding of the scale and proceedings.
Types of Aerial Photography Based on Technique
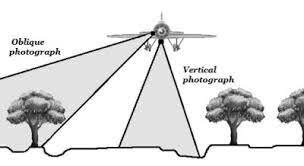
While the purpose of aerial photography often dictates the method or tool used, the technique plays an equally critical role in determining the final outcome of the shot. Different techniques provide varied perspectives and levels of detail, influencing the effectiveness of the imagery for its intended use. Among the myriad techniques available for aerial cameras, one of the most distinguished categories for aerial photographers is oblique aerial photography.
a. Oblique Aerial Photography

An oblique aerial photograph is taken with the camera aimed diagonally downward, rather than directly downwards like in vertical shots. The result of oblique aerial photographs is an image that resembles more closely what we see from an elevated viewpoint, like from a hilltop or a tall building, providing a more natural perspective. Within this technique, there are further classifications based on the angle at which the vertical photograph is oblique photos taken.
-
High-angle Oblique: In this technique, the camera angle is steep, but not directly downward. It captures a large portion of the horizon, giving a broad overview of the landscape. The high oblique aerial photographs are especially useful when the objective is to capture a wide area while retaining some depth perception.
-
Low-angle Oblique: The camera is tilted at a shallower angle, capturing less of the horizon and more of the foreground. Low oblique photographs is particularly effective when the focus is on a specific object or area, providing a detailed view while still offering a sense of scale and context.
b. Vertical Aerial Photography

Vertical aerial photography involves an unmanned aircraft and capturing vertical aerial photographs with the camera aimed directly downwards, perpendicular to the earth’s surface. This technique produces an overhead view that is especially useful for mapping, remote sensing, reconnaissance surveys surveying vertical photography, and planning purposes.
-
Advantages: Offers a consistent scale, making measurements straightforward and accurate.
-
Limitations: Lacks the depth and perspective seen in oblique shots, and might miss vertical or nearly vertical features like the sides of buildings.
c. Panchromatic, Infrared, and Multispectral Photography
This technique is distinguished not by ground distance or by the camera’s angle but by the type of light the camera sensor captures.
-
Panchromatic: Captures images in black and white, sensitive to all colors of light. These images are often sharper than colored images because all sensor pixels are used for luminance.
-
Infrared: Records infrared light, which is beyond the spectrum visible to the human eye. It’s invaluable for environmental studies as it can indicate plant health, water sources, and more.
-
Multispectral: Captures light in multiple specific wavelengths, both in the visible and invisible spectrum. Used extensively in agriculture to monitor crop health and in environmental monitoring.
d. Orthophotography
An orthophoto is a still aerial image or photograph that has been “corrected” to remove all the optical and positional distortions inherent in aerial photography. This is done using the principles of photogrammetry and involves using elevation data to adjust vertical position of the photo so that it’s accurate and to scale, just like a map.
-
Advantages: Provides a true-to-scale image that can be used reliably for measurements and planning.
-
Process: Often involves combining images, adjusting for elevation changes, and removing distortions from camera optics and tilt.
-
Applications: Widely used in GIS (Geographic Information Systems), urban planning, and land surveying.
Types of Aerial Photography based on scale
Scale in aerial photography is a fundamental concept, determining both the area covered by an image and the level of detail it can depict. The scale of an aerial photograph is essentially a representation of the relationship between a particular distance on the photo and the corresponding actual distance and same area on the ground. Understanding this relationship is crucial, as it provides context to the viewer and guides professionals in diverse fields, from urban planning to environmental conservation. Based on scale, aerial photographs can be broadly classified into two main categories:
Large Scale Aerial Photographs:
-
Definition: These are photographs wherein the ground features appear larger. A large scale photograph covers a smaller area but in greater detail.
-
Details: Objects in large scale photos are clearer and more defined, making them suitable for analyzing specific sites or features.
-
Usage: Commonly used in projects that require intricate details such as construction planning, detailed environmental studies, or archeological site analyses.
-
Example: An aerial photograph capturing a construction site, showing the intricate layout of equipment, personnel, and structures.
Small Scale Aerial Photographs:
-
Definition: In the small scale aerial photography, the ground features appear smaller, covering a much larger area but with less detail.
-
Overview: These photos provide a broader perspective, useful for getting a general overview or understanding the context.
-
Usage: Suited for projects like regional planning, watershed analysis, or large-scale land cover mapping.
-
Example: An aerial photograph capturing an entire city or a vast agricultural expanse.
Benefits and Limitations of Aerial Photograph

Aerial photography has revolutionized the way we perceive, analyze, and interpret our surroundings, offering a unique bird’s-eye view of the world. From urban planning to environmental monitoring, its applications are extensive. However, like any technology or method, aerial photography comes with its set of advantages and drawbacks. Here’s a closer look into the benefits and limitations of aerial photographs based this fascinating domain:
Benefits:
-
Broader Perspective: Aerial photography offers a comprehensive view of landscapes, properties, and events, providing context and scale that ground-based photography cannot match.
-
Accessibility: Areas that are challenging or impossible to reach on foot, such as mountaintops, dense forests, or remote islands, become accessible through aerial imaging.
-
Time Efficiency: Large areas can be covered in a relatively short amount of time, especially beneficial for surveys, mapping, and reconnaissance.
-
Versatility: With various techniques and equipment available, aerial photography can cater to diverse needs – from detailed topographic maps to stunning cinematic shots.
-
Safety: In hazardous areas, like disaster zones or conflict regions, aerial photography can gather crucial information without putting human lives at direct risk.
-
Innovative Data Collection: Especially with multispectral and infrared imaging, aerial photography can gather data not visible to the human eye, invaluable for fields like agriculture and environmental science.
Limitations:
-
Weather Dependencies: Adverse weather conditions, such as high winds, fog, or rain, can hamper or halt aerial photography operations, especially when using drones.
-
Legal Restrictions: Many countries have stringent regulations about where and how aerial photography, particularly drone usage, can be conducted. This includes no-fly zones around airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas.
-
Cost: While drone technology has become more affordable, high-end equipment, manned aircraft, and satellite-based photography can be expensive.
-
Technical Challenges: Achieving stable shots, especially in windy conditions or with fast-moving subjects, requires skill and often sophisticated stabilization equipment.
-
Privacy Concerns: Aerial photography can unintentionally capture private moments or sensitive information, leading to ethical and legal challenges.
-
Environmental Concerns: There can be potential disturbances to wildlife, especially when low-flying aircraft or drones are used in sensitive habitats.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Aerial Photography
As aerial photography continues to gain traction, especially with the increased accessibility of drones, it brings forth a series of legal and ethical dilemmas. These concerns highlight the need for photographers, businesses, and hobbyists to be well-versed in the regulations and moral considerations associated with this craft. Let’s delve into the key legal and ethical dimensions of aerial photography:
Privacy Concerns:
-
Intrusiveness: Aerial photography, especially with drones, can capture aerial photograph of private properties and individuals without their consent. This can be seen as invasive, potentially violating personal privacy rights.
-
Legal Precedents: In many countries, laws are evolving to protect individuals from unsolicited aerial surveillance. Photographers might be required to obtain permissions or avoid certain spaces to respect privacy.
Flight and Drone Regulations:
-
No-Fly Zones: Many areas, especially near airports, government buildings, or military installations, are designated as no-fly zones. Flying in these areas can attract hefty penalties or even criminal charges.
-
Altitude Restrictions: There are often height limits imposed on how high drones can fly to prevent interference with other aircraft.
-
Pilot Licensing: Many countries now mandate a license or certification for operating drones, especially for commercial purposes. This often requires passing an exam or undergoing training.
Ethical Considerations in Journalism:
-
Accuracy and Authenticity: Journalists have a responsibility to portray events truthfully. Manipulating aerial shots or taking them out of context can mislead the public.
-
Sensitivity: Aerial shots of disasters, crime scenes, or tragic events need to be taken and published with respect and consideration for the affected individuals and communities.
-
Public Interest vs. Privacy: While the public has a right to know, journalists must balance this with the potential harm or intrusion that might come from aerial coverage. For instance, publishing an aerial image of a celebrity’s private residence might not be justifiable in the same way as capturing a large public event.
In conclusion, the skyward perspective offered by aerial photography, while invaluable, comes with a set of responsibilities. Whether a professional photographer or a recreational drone enthusiast, it’s vital to stay informed about the legal landscape of aerial imagery and remain cognizant of the ethical implications of one’s actions. With a judicious approach, aerial photography can be a tool for insight, creativity, and positive impact.
Conclusion
The world of aerial photography is vast and varied, with many different techniques and technologies offering unique perspectives of our world. From traditional photographers using both oblique photographs like low oblique photographs or high oblique aerial photographs and vertical images to orthophotos, photogrammetry, infrared photography, large scale aerial photographs, satellite imagery, and high-altitude balloon captures, each type serves specific purposes and suits different applications.
The choice of aerial photography for any particular commercial advertising project largely hinges on the client’s requirements. For example, photos delineating the boundaries archaeological features of a plot of land would be significantly different from those promoting real estate or a luxury yacht. A seasoned aerial photographer, with a deep understanding of the diverse types of aerial photography, can take all these details into account to deliver the highest quality photos or videos tailored to each scenario.
When it comes to reliable, expert aerial photography services, look no further than JR Resolutions. We pride ourselves on delivering top-notch results every time. Our seasoned professionals will leverage their extensive knowledge to craft aerial photo and video packages customized to your needs, incorporating high-resolution footage and music for a dynamic look and feel and stunning photos. No matter the kind of aerial photos that you require, we ensure you get the most value for your investment.
If you’re ready to harness the power of drone technology and elevate your projects, be they construction, real estate, or other ventures, our article “The Complete Guide: Hiring a Drone Service”will serve as an invaluable resource. Dive into this comprehensive guide to unlock the full potential of drone services for your projects.



2 Responses
Great information on various Aerial imagery. Thanks
Very nice👍, thanks sir